Comprehensive care for digestive disorders by Dr. Akeel Alisa


Most people experience occasional heartburn or indigestion after a heavy meal, but when these symptoms occur frequently or interfere with daily life, they may indicate gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD).
Heartburn happens when stomach acid flows back into the oesophagus (the tube that connects your throat to your stomach). This acid reflux irritates the lining of the oesophagus, causing a burning sensation in the chest, often after eating or when lying down.
Indigestion (dyspepsia) refers to discomfort or pain in the upper abdomen, which may be associated with bloating, nausea, or early satiety. While often harmless, persistent indigestion can sometimes be a sign of an underlying digestive condition.
If these symptoms occur more than twice a week, you may have GORD and should seek specialist advice.
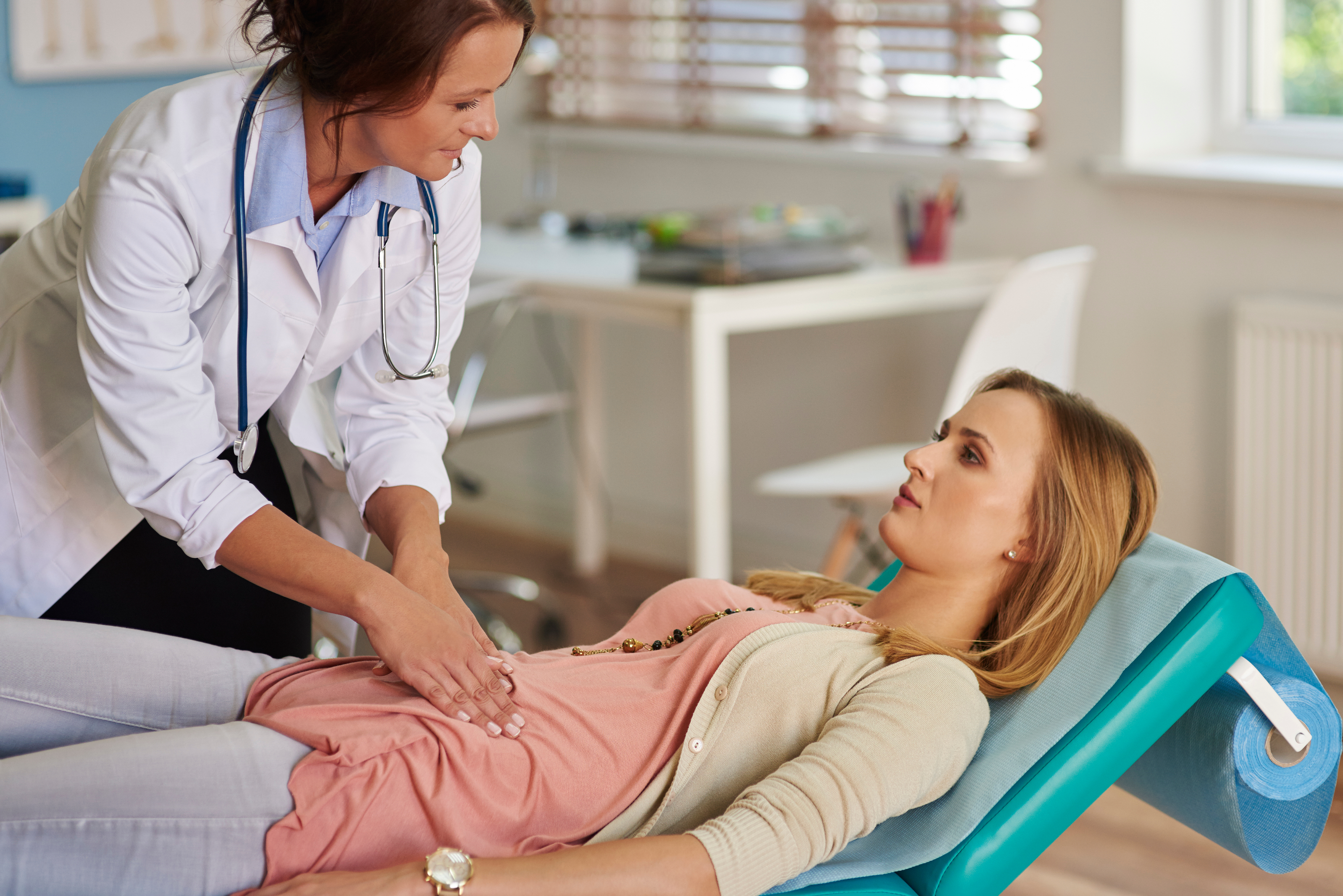
Several factors increase the likelihood of developing acid reflux and indigestion:
Common symptoms include:
You should seek specialist care if you experience:
These warning signs may indicate complications or another underlying digestive condition that requires prompt evaluation.
A gastroenterologist can carry out investigations to confirm the cause of your symptoms. These may include:
These tests help identify whether reflux is causing inflammation, ulcers, narrowing of the oesophagus, or precancerous changes such as Barrett’s oesophagus.
In cases where medication is not effective, or when complications develop, specialist procedures may be considered:
Chronic acid reflux and indigestion can lead to complications, including:
Early diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent these long-term risks.
While mild heartburn can often be managed with over-the-counter remedies, persistent or severe symptoms require expert evaluation. A gastroenterologist can:
 5.0 Rating on Doctify
5.0 Rating on Doctify
Read testimonials from patients who have experienced Dr Alisa's expert care.

My consultation with Dr Akeel Alisa was highly satisfactory and he was very thorough. The Gastroscopy procedure was performed satisfactorily with no pain or discomfort at all. I am very pleased with treatment received so far.
Verified Patient

I was fully vaccinated investigated by Dr Akeel Alisa and I was reassured. My endoscopy and colonoscopy were straight forward and painless. I am very happy with the care I received.
Verified Patient

Dr Akeel Alisa and Nursing team at Cromwell Hospital Endoscopy team offered me great care and all was perfect. Well pleased.
Verified Patient